As I explained before, whenever you can’t connect to a WiFi network that previously worked, a good start is to tell Windows to forget the WiFi connection (right-click the connection). Unfortunately, this means Windows will also forget the password. Thus, you will find yourself again bothering the person who is managing the WiFi password.
In Windows 8, you could just click the WiFi icon on the systray and right-click the WiFi connection to access the View connection properties dialog. For some reason, Microsoft removed this feature in Windows 8.1.
View connection properties option: no longer available in Windows 8.1
However, in Windows 8.1, two other ways exist to access the WiFi password. You’ll find one way in the Network and Sharing Center for your current connection, and you can also use the netsh command to view the connection properties of previous WiFi connections.
1. Right-click the WiFi symbol in the system tray and select Open Network and Sharing Center.
2.Click Change adapter settings.
Right-click the WiFi adapter. In the context menu, navigate to Status.
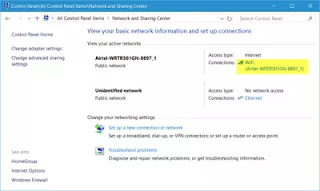
In the WiFi Status dialog, click Wireless Properties.
Click the Security tab and then check Show characters.
You now see the WiFi password of your current connection. Doing so takes a few more clicks than in Windows 8, but you won’t have to do this often.
If you are more the type-type type, you will prefer the netsh command anyway. This method allows you to find not only the WiFi password of your current connection but also that of previous connections. The syntax of the command looks like this:
netsh wlan show profile name="ConnectionName" key=clear
Finding WiFi password on the command line with netsh
Notice that you only need the quotation marks for the connection name (profile name) when the name contains a blank. You can find the password in the Security settings section next to Key Content.
To get a list of your previous WiFi connections, type this command:
netsh wlan show profiles
If you prefer a GUI, you can also list all of your previous WiFi connections in Windows 8.1 in the PC Settings:
WIN + C > Settings > Change PC settings > Manage known networks (under your current connection)
In Windows 8, you could just click the WiFi icon on the systray and right-click the WiFi connection to access the View connection properties dialog. For some reason, Microsoft removed this feature in Windows 8.1.
View connection properties option: no longer available in Windows 8.1
However, in Windows 8.1, two other ways exist to access the WiFi password. You’ll find one way in the Network and Sharing Center for your current connection, and you can also use the netsh command to view the connection properties of previous WiFi connections.
View WiFi password of current connection
1. Right-click the WiFi symbol in the system tray and select Open Network and Sharing Center.
2.Click Change adapter settings.
Right-click the WiFi adapter. In the context menu, navigate to Status.

In the WiFi Status dialog, click Wireless Properties.
Click the Security tab and then check Show characters.
You now see the WiFi password of your current connection. Doing so takes a few more clicks than in Windows 8, but you won’t have to do this often.
Find WiFi password of previous connections
If you are more the type-type type, you will prefer the netsh command anyway. This method allows you to find not only the WiFi password of your current connection but also that of previous connections. The syntax of the command looks like this:
netsh wlan show profile name="ConnectionName" key=clear
Finding WiFi password on the command line with netsh
Notice that you only need the quotation marks for the connection name (profile name) when the name contains a blank. You can find the password in the Security settings section next to Key Content.
To get a list of your previous WiFi connections, type this command:
netsh wlan show profiles
If you prefer a GUI, you can also list all of your previous WiFi connections in Windows 8.1 in the PC Settings:
WIN + C > Settings > Change PC settings > Manage known networks (under your current connection)












No comments:
Post a Comment